This study suggests that changes in plasma growth hormone mediators are associated with loss of glycemic control in youth-onset T2D, with IGF-1 associated with lower risk and GHR and IGFBP-1 associated with increased risk.

Out-of-Pocket Costs Among Commercially Insured Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity: Comparison Between Ozempic and Sleeve Gastrectomy
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38775477/
Within 2 years of starting treatment, OOP healthcare costs were significantly lower among individuals who had a SG versus those treated with Ozempic.
Within 2 years of starting treatment, out-of-pocket healthcare costs were significantly lower among individuals who had sleeve gastrectomy versus those treated with semaglutide.

Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors and Cardiovascular Protection Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: a Systematic Review
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38766320/
Background: Accumulating evidence has demonstrated the positive effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors in managing patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). SGLT2 inhibitors protect patients with T2DM from cardiovascular...
SGLT2 inhibitors have beneficial CV effects in patients with type 2 diabetes and should be incorporated into their management.

A Comprehensive Analysis of Clinical, Biochemical, and Polysomnographic Characteristics in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus With and Without Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Background: Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) has been a significant contributor to mortality all across the globe. The most attributing factors to pathogenesis are metabolic syndrome, obesity, diabetes, and so on,...
Researchers found a positive correlation between the waist-to-hip ratio and the prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea in persons with type 2 diabetes.
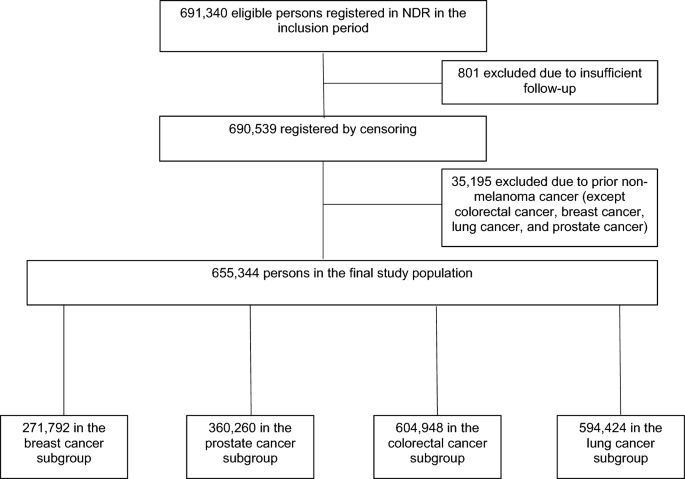
Diabetes-Related Risk Factors and Survival Among Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes and Breast, Lung, Colorectal, or Prostate Cancer
Source : https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-61563-9
Premature death in diabetes is increasingly caused by cancer. The objectives were to estimate the excess mortality when individuals with type 2 diabetes(T2D) were diagnosed with cancer, and to examine...
Smoking and lack of exercise emerged as the most influential modifiable risk factors associated with mortality.

