
Out-of-Pocket Costs Among Commercially Insured Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity: Comparison Between Ozempic and Sleeve Gastrectomy
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38775477/
Within 2 years of starting treatment, OOP healthcare costs were significantly lower among individuals who had a SG versus those treated with Ozempic.
Within 2 years of starting treatment, out-of-pocket healthcare costs were significantly lower among individuals who had sleeve gastrectomy versus those treated with semaglutide.

Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors and Cardiovascular Protection Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: a Systematic Review
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38766320/
Background: Accumulating evidence has demonstrated the positive effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors in managing patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). SGLT2 inhibitors protect patients with T2DM from cardiovascular...
SGLT2 inhibitors have beneficial CV effects in patients with type 2 diabetes and should be incorporated into their management.

A Comprehensive Analysis of Clinical, Biochemical, and Polysomnographic Characteristics in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus With and Without Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Background: Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) has been a significant contributor to mortality all across the globe. The most attributing factors to pathogenesis are metabolic syndrome, obesity, diabetes, and so on,...
Researchers found a positive correlation between the waist-to-hip ratio and the prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea in persons with type 2 diabetes.
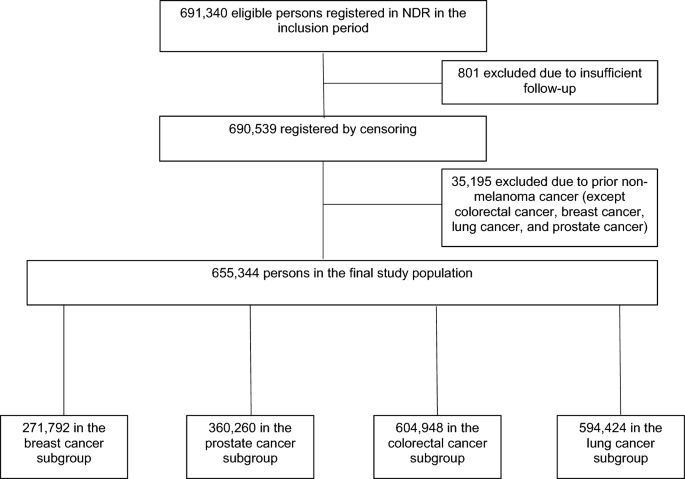
Diabetes-Related Risk Factors and Survival Among Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes and Breast, Lung, Colorectal, or Prostate Cancer
Source : https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-024-61563-9
Premature death in diabetes is increasingly caused by cancer. The objectives were to estimate the excess mortality when individuals with type 2 diabetes(T2D) were diagnosed with cancer, and to examine...
Smoking and lack of exercise emerged as the most influential modifiable risk factors associated with mortality.

Understanding the Gap Between Guidelines and Influenza Vaccination Coverage in People With Diabetes: a Scoping Review
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38706547/
Influenza vaccination coverage in people with diabetes remains low despite recommendations and evidence on vaccine effectiveness. Motivators and barriers as well as several socio-demographic and clinical factors have been identified...
Determinants such as advanced age, presence of comorbidities and advice from healthcare professionals were associated with increased vaccination uptake.

