
Glycaemic Control Achieves Sustained Increases of Circulating Endothelial Progenitor Cells in Patients Hospitalized for Decompensated Diabetes: An Observational Study - Diabetes Therapy
Source : https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13300-022-01273-5
Background and Aim Diabetes reduces the levels of circulating endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs), which contribute to vascular homeostasis. In turn, low EPCs levels predict progression of chronic complications. Several studies...
Conclusion: In individuals hospitalized for decompensated diabetes, insulin therapy rapidly increases EPC levels for up to 2 months. EPC defect, reflecting impaired vascular repair capacity, may be reversible in the early diabetes stages.

The role of oral semaglutide in managing type 2 diabetes in Indian clinical settings: Addressing the unmet needs
Source : https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1871402122001229?via=ihub
Effective, safe, and easily accessible antidiabetics with cardiovascular protection are much needed in India. * Oral semaglutide has better glycemic and weight control and decreases CV risk, best suited for...
Conclusions: Currently, there is no data available on oral semaglutide in Indian clinical settings. However, significant improvements in glycemic control, cardiac and renal benefits, as well as weight loss across clinical trials should encourage clinicians to prioritize oral semaglutide over other antidiabetic agents.
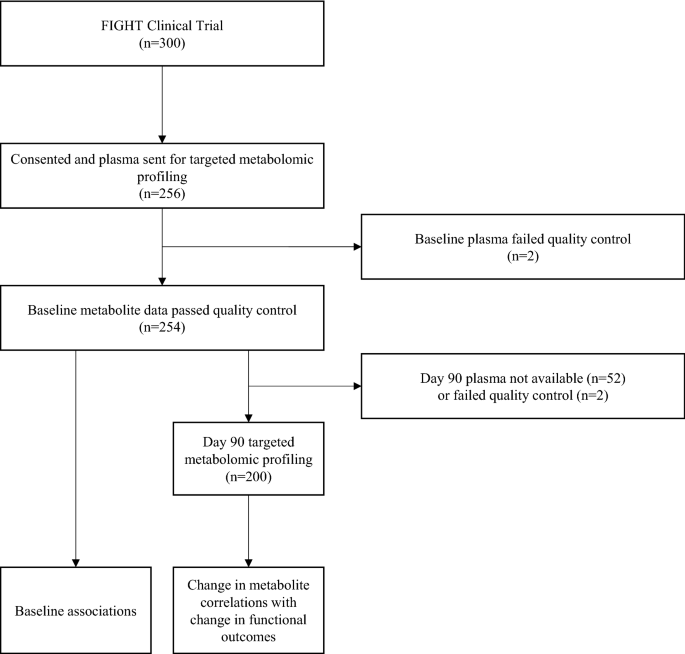
Plasma metabolites associated with functional and clinical outcomes in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction with and without type 2 diabetes - Scientific Reports
Source : https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-12973-0
Heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) is increasingly treated with medications for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Whether metabolic derangements in HFrEF and T2DM are associated with differential outcomes...
Conclusion/Relevance: We identified metabolites of BCAA, urea cycle and fatty acid metabolism as biomarkers of HFrEF outcomes, with observed differences in HFrEF patients with T2DM. Such biomarkers might enable future diagnostic or therapeutic interventions in individuals with HFrEF and T2DM.

Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists: A Medication for Obesity Management - Current Atherosclerosis Reports
Source : https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11883-022-01041-7
Purpose of Review The burden of obesity worldwide is high and projected to rise. Obesity increases the risk of several cardiovascular diseases and cardiometabolic risk factors; hence, utilizing effective long-term...
Summary: GLP-1RAs have robust weight loss benefits and are expected to have a critical role in the management of obesity in the coming years. Upcoming studies will evaluate the durability of weight loss achieved with GLP-1RAs and the impact on cardiovascular outcomes.
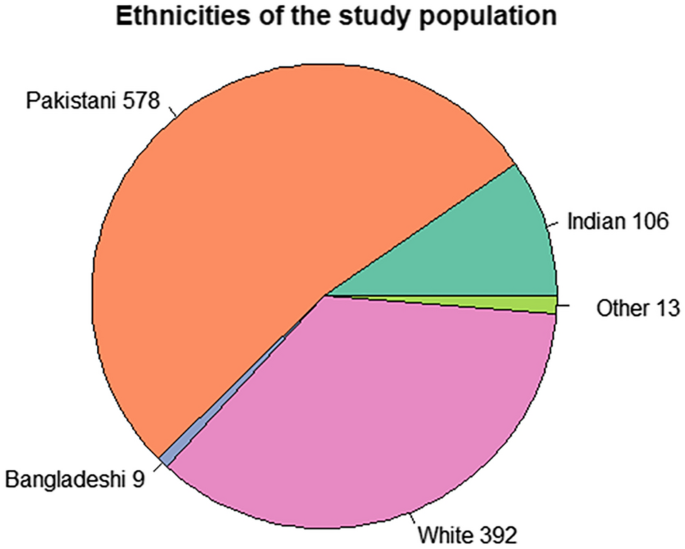
Disparity in association of obesity measures with ankle and brachial systolic blood pressures in Europeans and South Asians - Scientific Reports
Source : https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-13372-1
Obesity causes increases in brachial systolic-blood-pressures (SBP), risks of type 2 diabetes (T2DM) and cardiovascular diseases (CVD). Brachial and ankle SBPs have differential relationship with T2DM and CVD. Our objective...
Relevance: Brachial and ankle SBPs have differential relationship with T2DM and CVD. Our objective was to study the relationship of obesity measures with brachial and ankle SBPs.

