Gray matter volumetric correlates of attention deficit and hyperactivity traits in emerging adolescents - Scientific Reports
Source : https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-15124-7
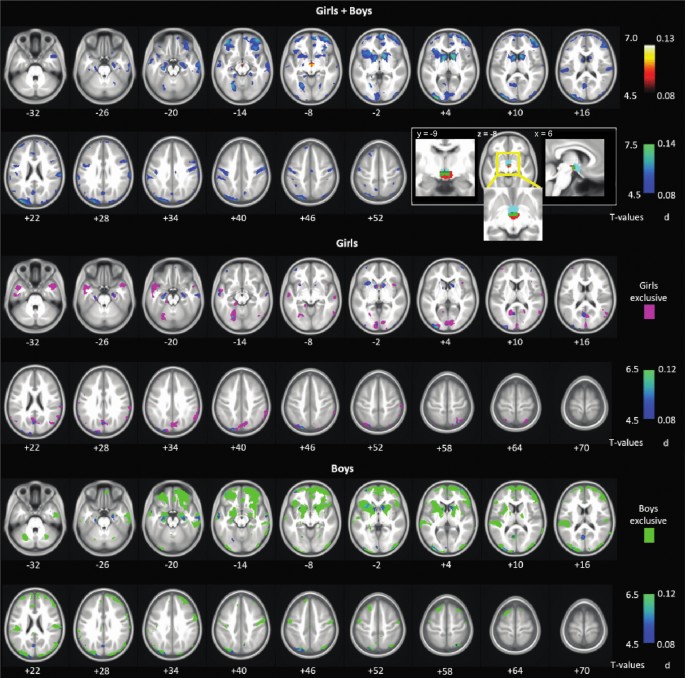
Previous research has demonstrated reduction in cortical and subcortical, including basal ganglia (BG), gray matter volumes (GMV) in individuals with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), a neurodevelopmental condition that is...
Conclusion: Together, these findings confirm volumetric deficits in children with more prominent ADHD traits. Highly heritable in both girls and boys and potentially more significant in boys than in girls, the structural deficits underlie diminished capacity in working memory and potentially other cognitive deficits in ADHD.
Conclusions and Relevance: In this study, genetic liability to neurodevelopmental conditions that is passed from mothers to children was associated with several pregnancy-related factors and may therefore confound associations between these pregnancy-related factors and offspring neurodevelopment that have previously been thought to be causal....

Optimising the management of children with concomitant bladder dysfunction and behavioural disorders - European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry
Source : https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00787-022-02016-4
Bladder dysfunction and behavioural disorders in children are commonly concomitant; hence, it is difficult to treat each in isolation. Pharmacotherapy is common treatment for behavioural disorders, and these medications may...
Conclusion/Relevance: This review identifies useful factors that may assist clinicians with predicting unintended bladder effects following initiation of behavioural pharmacotherapy to facilitate the best approach to the treatment of bladder dysfunction in children with behavioural disorders. With this evidence, we have provided a useful...
-
 ADHD Connect3yrKey Points • Source: European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry • Conclusion: “This review identifies useful factors that may assist clinicians with predicting unintended bladder effects following initiation of behavioural pharmacotherapy to facilitate the best Show More
ADHD Connect3yrKey Points • Source: European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry • Conclusion: “This review identifies useful factors that may assist clinicians with predicting unintended bladder effects following initiation of behavioural pharmacotherapy to facilitate the best Show More

Lifetime psychiatric diagnoses among adolescents with severe conduct problems - A register-based follow-up study
Source : https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0145213422002976?via=ihub
Both delinquency and out-of-home care (OOHC) are associated with a wide spectrum of psychiatric disorders. Reform schools (RS) are Finnish OOHC institutions for adolescents with severe conduct problems. We investigated...
Conclusions: RS background associates with an excess of psychiatric disorders, which adds to the burden of other known risk factors for adult age well-being. Effective screening and intervention for psychiatric problems should be available both during the RS placement and after-care.

Genetic Relationships between Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder, Autism Spectrum Disorder, and Intelligence - PubMed
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35764056/
Our results suggest that ADHD is associated with inheriting a reduced set of low-intelligence alleles, whereas ASD results from incongruous effects from a mixture of high-intelligence and low-intelligence contributing alleles...
Conclusion: Our results suggest that ADHD is associated with inheriting a reduced set of low-intelligence alleles, whereas ASD results from incongruous effects from a mixture of high-intelligence and low-intelligence contributing alleles summed up with additional, ASD-specific risk variants not associated with intelligence.
