
Immunologic Interplay Between HIV/AIDS and COVID-19: Adding Fuel to the Flames? - Current HIV/AIDS Reports
Source : https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11904-023-00647-z
Purpose of Review HIV/AIDS and COVID-19 have been the major pandemics overwhelming our times. Given the enduring immune disfunction featuring people living with HIV (PLWH) despite combination antiretroviral therapy (cART),...
Summary: Scarce immunovirological control appears to be the major driver of weak immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection/vaccination and worse COVID-19 outcomes in PLWH. Therefore, such individuals should be prioritized for vaccination and should receive additional vaccine doses. Furthermore, given the potentially higher risk of developing...
Faster lung function decline in people living with HIV despite adequate treatment: a longitudinal matched cohort study
Source : https://thorax.bmj.com/content/early/2023/01/13/thorax-2022-218910
Introduction Chronic lung disease is common among people living with HIV (PLWH). We hypothesised that PLWH receiving antiretroviral therapy (ART) have faster lung function decline than matched controls.
Conclusion: Well-treated PLWH have faster lung function decline than controls and smoking seems to modify this association, suggesting that smoking may lead to more rapid lung function decline in PLWH than in controls.

HIV infection of non-classical cells in the brain - Retrovirology
Source : https://retrovirology.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12977-023-00616-9
HIV-associated neurological disorders (HAND) affect up to 50% of people living with HIV (PLWH), even in the era of combination antiretroviral therapy (cART). HIV-DNA can be detected in the cerebral...
Relevance: HIV eradication strategies that target persistently infected glia cells will likely be needed to achieve HIV cure.
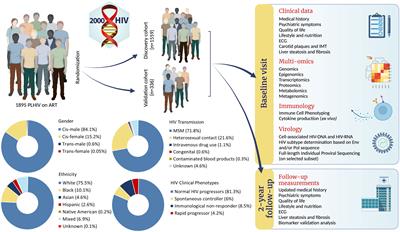
The 2000HIV study: Design, multi-omics methods and participant characteristics
Source : https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2022.982746/full
BackgroundEven during long-term combination antiretroviral therapy (cART), people living with HIV (PLHIV) have a dysregulated immune system, characterized by persistent immune activation, accelerated immune ageing and increased risk of non-AIDS...
Conclusion: The 2000HIV study established a cohort of 1895 PLHIV that employs multi-omics to discover new biological pathways and biomarkers to unravel non-AIDS comorbidities, extreme phenotypes and the latent viral reservoir that impact the health of PLHIV. The ultimate goal is to contribute to a more personalized approach to the best standard...

Indirect Treatment Comparisons of Lenacapavir plus Optimized Background Regimen Versus Other Treatments for Multi-Drug Resistant HIV - PubMed
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36566886/
Available evidence on the efficacy and effectiveness of different therapies in HTE PWH is sparse. This is the first analysis that provides comparative treatment estimates which can be used alongside...
Conclusion: LEN OBR has statistically significantly greater odds of VS at Week 24-28 than its comparators and represents a novel treatment for people with MDR HIV.

