The Influence of Habitual Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior on Objective and Subjective Hot Flashes at Midlife
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38530999/
These data provide support for relations between sedentary time, physical activity, and hot flashes and highlight the importance of using objective and subjective assessments to better understand the 24-hour hot...
Replacing 1 hour of sitting with 1 hour of vigorous activity was associated with a 100% increase in subjectively reported but not objectively measured waking hot flashes.
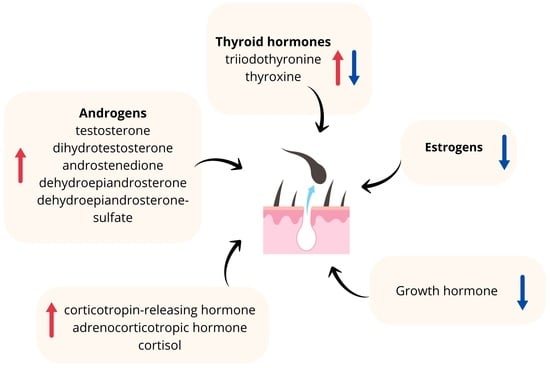
The Hormonal Background of Hair Loss in Non-Scarring Alopecias
Source : https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9059/12/3/513
Hair loss is a common clinical condition connected with serious psychological distress and reduced quality of life. Hormones play an essential role in the regulation of the hair growth cycle....
Hair loss may occur in the case of estrogen deficiency, appearing naturally during menopause.
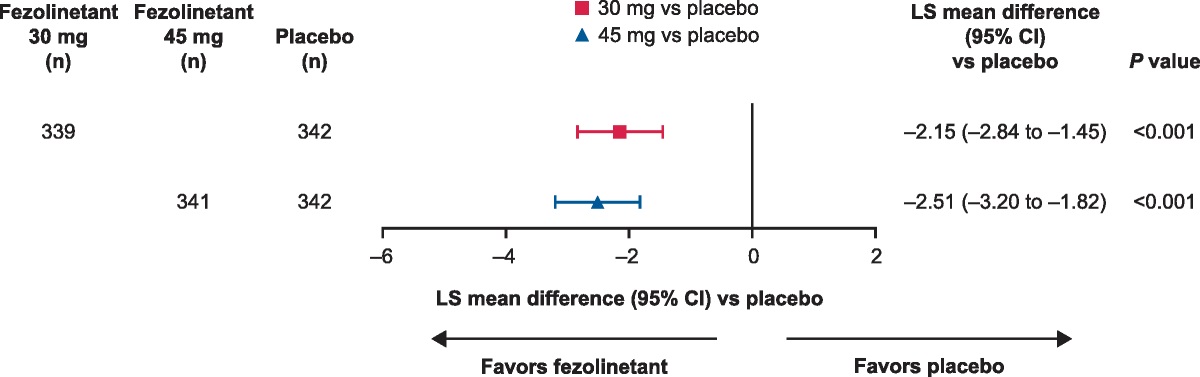
Fezolinetant Treatment of Moderate-to-Severe Vasomotor Symptoms Due to Menopause: Effect of Intrinsic and Extrinsic Factors in Two Phase 3 Studies (SKYLIGHT 1 and 2)
sing pooled 12-week data from SKYLIGHT 1 and 2. Methods SKYLIGHT 1 and 2 were two phase 3, randomized, double-blind studies conducted from July 2019 to August 2021 (SKYLIGHT 1)...
Efficacy was most notable for participants who self-identify as Black, current smokers, and current alcohol users.
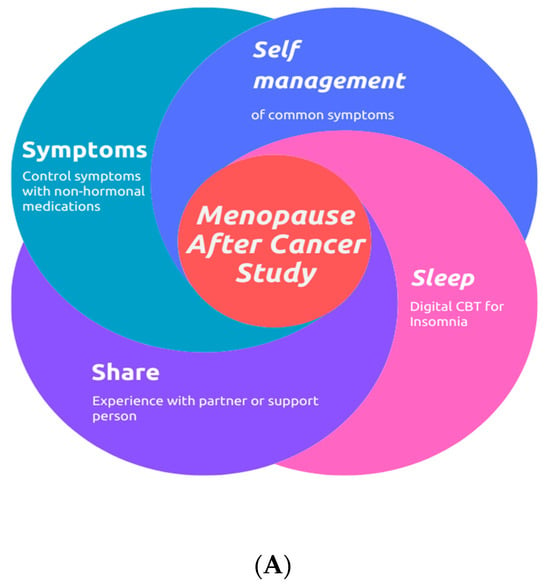
Multimodal, Technology-Assisted Intervention for the Management of Menopause After Cancer Improves Cancer-Related Quality of Life-Results From the Menopause After Cancer (Mac) Study
Source : https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/16/6/1127
Background: Vasomotor symptoms (VMSs) associated with menopause represent a significant challenge for many patients after cancer treatment, particularly if conventional menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) is contraindicated.
At least 50% reductions were noticed in the frequency of vasomotor symptoms as well as the degree of bother/interference of vasomotor symptoms at 6 months.
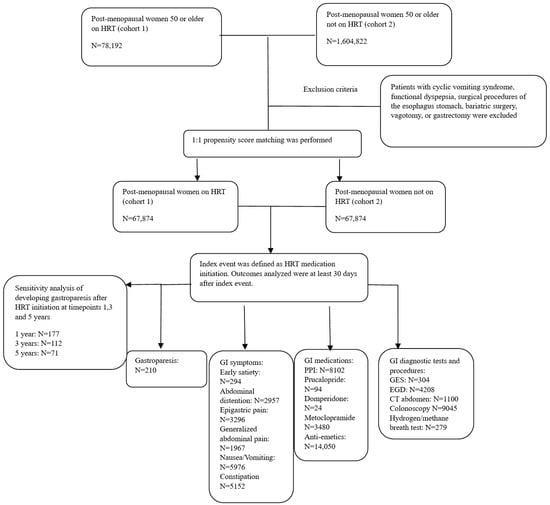
The Association Between Hormone Replacement Therapy and Gastroparesis in Post-Menopausal Women: a Worldwide Database Analysis
Source : https://www.mdpi.com/2075-4426/14/3/275
Female sex hormones have been hypothesized to influence the higher prevalence of gastroparesis in females. This study investigated the effects of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) on gastroparesis and its related...
Hormone replacement therapy was associated with increased GI symptoms, including early satiety, domperidone use, and undergoing gastric emptying studies.





