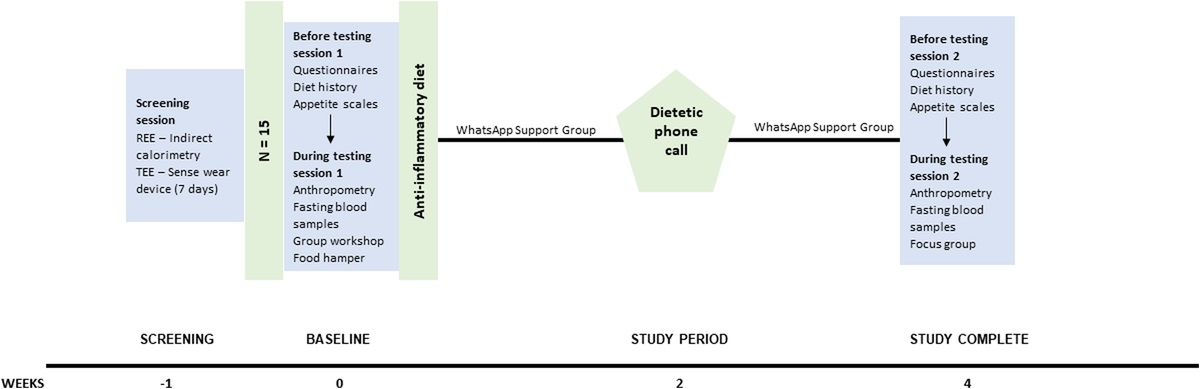
Investigating the efficacy and feasibility of using a whole-of-diet approach to lower circulating levels of C-reactive protein in postmenopausal women: a mixed methods pilot study
protein in weight stable postmenopausal women with abdominal obesity. Methods This mixed-methods pilot study used a single arm pre-post design. Thirteen women followed a 4-week anti-inflammatory, dietary intervention, optimizing consumption...
Conclusion: Weight-neutral dietary interventions targeting inflammation can improve metabolic markers and may be a viable strategy for CVD risk reduction in postmenopausal women. To determine effects on inflammatory status, a fully powered and longer-term randomized controlled trial is required.
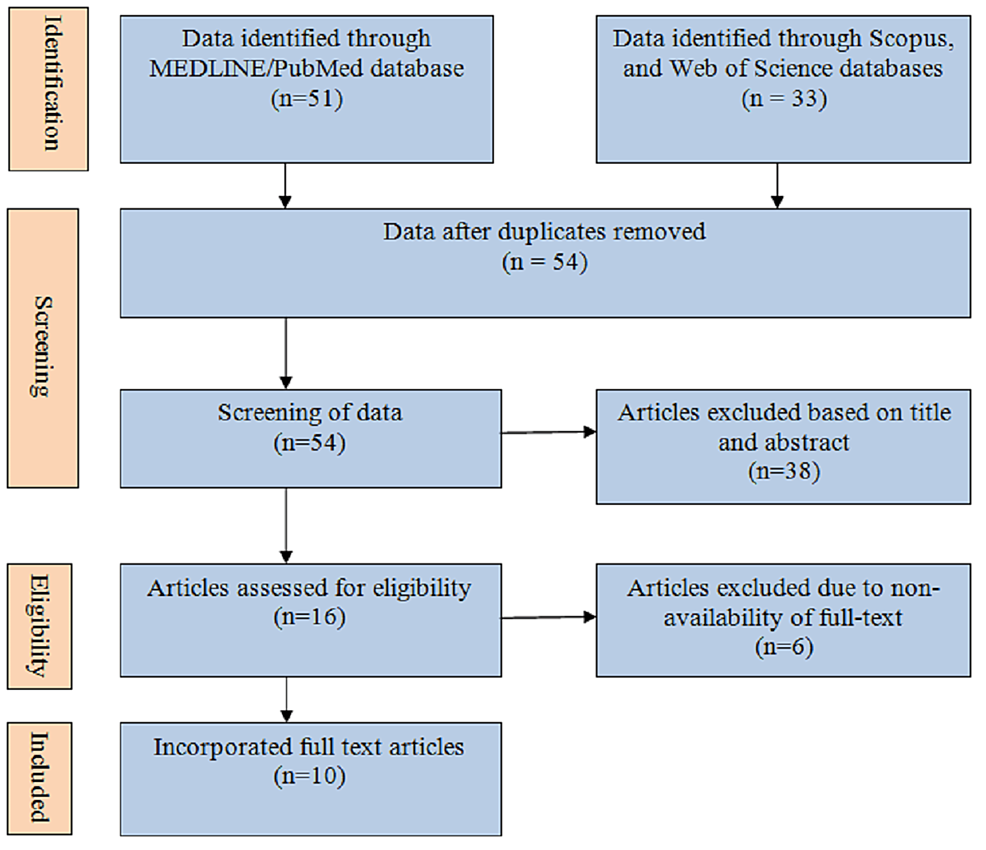
Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome and Its Association With Menopausal Symptoms in Post-Menopausal Women: A Scoping Review
Complex metabolic dysregulation leads to metabolic syndrome (MetS) causing various symptoms such as type II diabetes, central obesity, cardiovascular diseases (CVD), altered glucose metabolism, hypertension, and dyslipidemia, and is thought...
Conclusion: This review concludes that MetS is more common in post-menopausal women and are more likely to experience somatic complaints and a positive correlation of vasomotor symptoms with MetS, in comparison to pre-menopausal women which is due to estrogen shortage and fat redistribution. Additionally, in older and obese women, the...
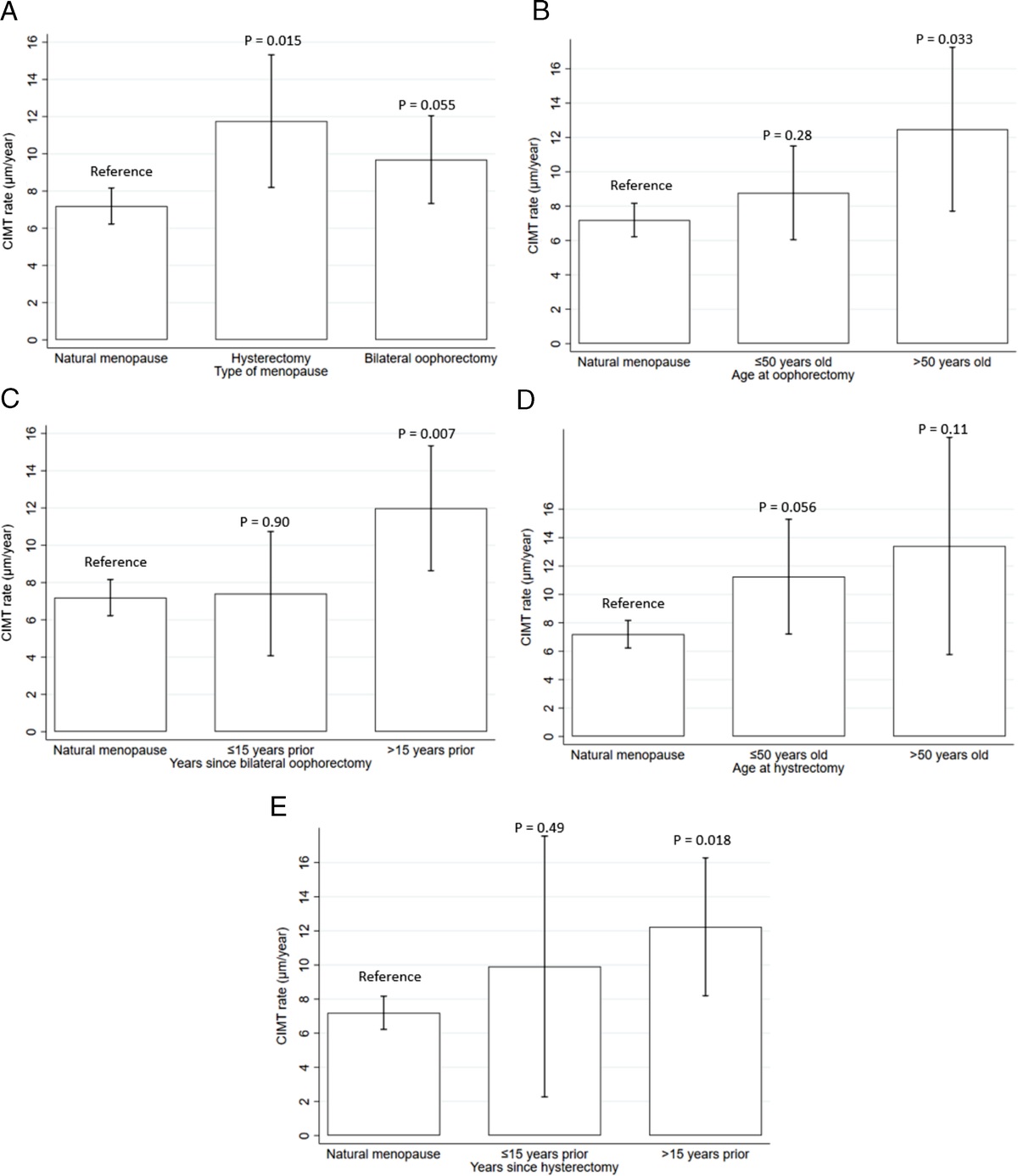
The association of hysterectomy with or without ovarian conservation with subclinical atherosclerosis progression in healthy postmenopausal women
to hormone therapy or placebo in the Early versus Late Intervention Trial with Estradiol (ELITE), which was conducted from July 2005 to February 2013. Subclinical atherosclerosis progression was measured as...
Conclusion: Hysterectomy with bilateral oophorectomy and ovarian conservation were associated with greater subclinical atherosclerosis progression relative to natural menopause. The associations were stronger for later age and longer time since oophorectomy/hysterectomy. Further research should continue to examine long-term atherosclerosis...
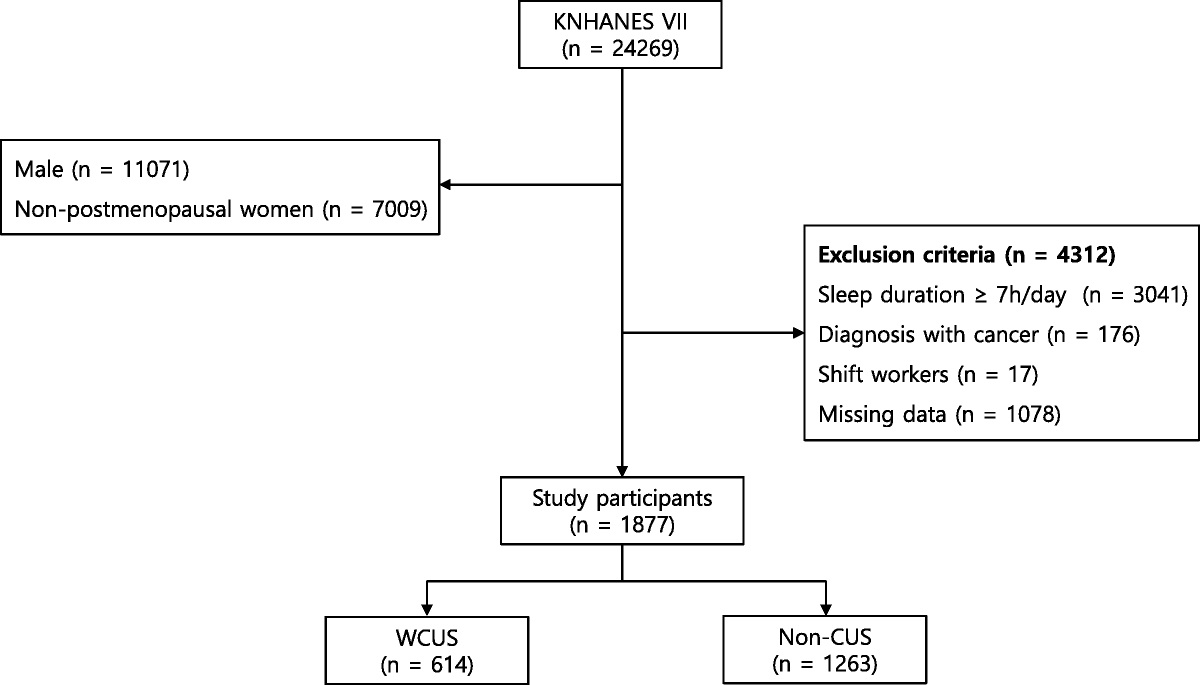
Association between weekend catch-up sleep and hyperuricemia with insufficient sleep in postmenopausal Korean women: a nationwide cross-sectional study
d with adequate sleep duration, which is related to a low risk of hyperuricemia. Considering that it is difficult for people to get enough sleep in modern society, this study...
Conclusions: Weekend catch-up sleep had a decreased prevalence of hyperuricemia in postmenopausal women with sleep deprivation.
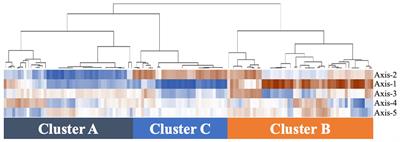
Etiology of recurrent cystitis in postmenopausal women based on vaginal microbiota and the role of Lactobacillus vaginal suppository
Source : https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2023.1187479/full
BackgroundThe vaginal microbiota can be altered by uropathogenic bacteria associated with recurrent cystitis (RC), and the vaginal administration of Lactobacillus have suggested certain effects to prevent RC. The relationship between...
Conclusion: The present study demonstrated that the vaginal microbiota in postmenopausal women with RC is essentially different from that of postmenopausal women with uncomplicated cystitis. Therefore, vaginal dysbiosis is likely associated with RC because the vagina serves as a reservoir of enteric bacteria, from which cystitis becomes...





