Prepregnancy Maternal Obesity and Infant Neurodevelopmental Outcomes in Latino Infants
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38600046
Managing maternal obesity pre-pregnancy is crucial for improving infant neurodevelopmental outcomes, especially in low-income Latino families. Promoting healthy weight and enhancing infant diet quality can enhance neurodevelopment in these populations.
Prepregnancy BMI showed significant negative associations with child cognitive scores and language scores at 24 months.

Timing of Moderate to Vigorous Physical Activity, Mortality, Cardiovascular Disease, and Microvascular Disease in Adults With Obesity
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38592034/
Aerobic MVPA bouts undertaken in the evening were associated with the lowest risk of mortality, CVD, and MVD. Timing of physical activity may play a role in the future of...
Similar patterns were observed for CVD and microvascular disease incidence rates, with evening moderate to vigorous physical activity associated with the lowest risk of CVD and microvascular disease.
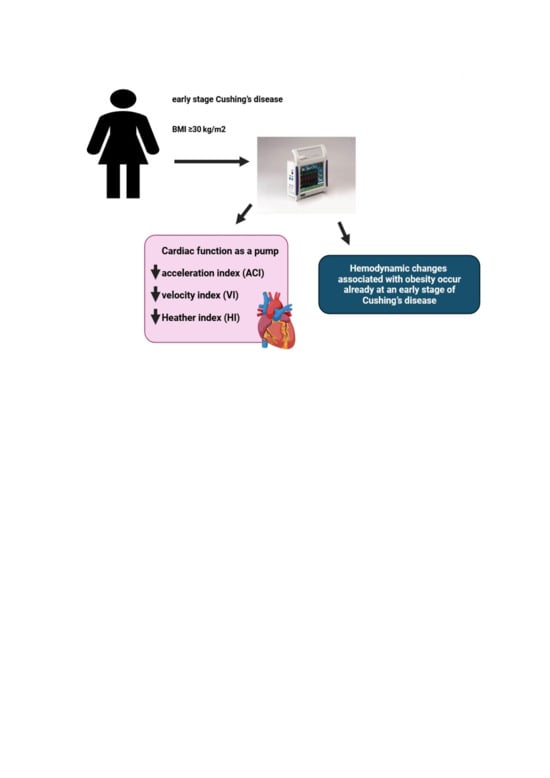
Obesity-Related Hemodynamic Alterations in Patients With Cushing's Disease
Source : https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/13/6/1658
Background: Cushing's disease (CD) is associated with a specific form of metabolic syndrome that includes visceral obesity, which may affect cardiovascular hemodynamics by stimulating hypercortisolism-related metabolic activity. The purpose of...
Use of novel diagnostic modalities demonstrated that excessive fat accumulation in young and middle-aged patients with Cushing disease, already at the early stages of the disease, is associated with some hemodynamic changes in the CV system.

Efficacy and Safety of Tirzepatide in Overweight and Obese Adult Patients With Type 1 Diabetes
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38512447/
In this pilot (off-label) study, we conclude that tirzepatide facilitated an average 18.5% weight loss (>46 pounds) and improved glucose control in OW/OB patients with T1D at one year. For...
There were significantly larger declines in BMI and weight in the treated group than controls across all time points among those in whom data were available.
Mean changes in bodyweight from baseline to week 46 were –6.2%, –12.5%, –13.2%, –14.9%, and –2.8%.






