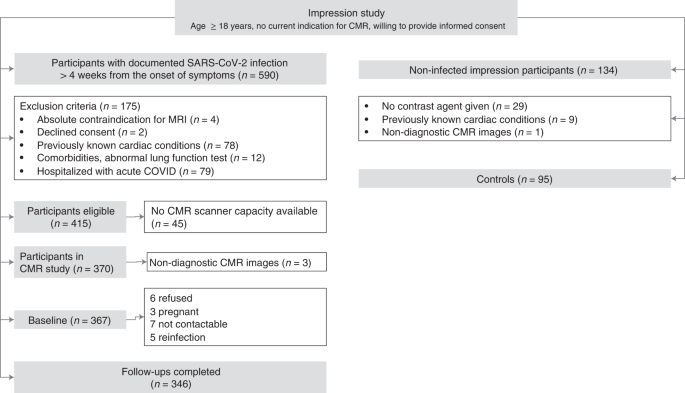
Long-term cardiac pathology in individuals with mild initial COVID-19 illness - Nature Medicine
Source : https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-022-02000-0
Cardiac symptoms are increasingly recognized as late complications of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection in previously well individuals with mild initial illness, but the underlying pathophysiology leading...
Ongoing inflammatory cardiac involvement may, at least in part, explain the lingering cardiac symptoms in previously well individuals with mild initial COVID-19 illness.

Clinical, Virologic, and Immunologic Evaluation of Symptomatic Coronavirus Disease 2019 Rebound Following Nirmatrelvir/Ritonavir Treatment - PubMed
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36200701/
Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir treatment does not impede adaptive immune responses to SARS-CoV-2. Clinical rebound corresponds to development of a robust antibody and T-cell immune response, arguing against a high risk of disease...
Conclusions: Nirmatrelvir/ritonavir treatment does not impede adaptive immune responses to SARS-CoV-2. Clinical rebound corresponds to development of a robust antibody and T-cell immune response, arguing against a high risk of disease progression. The presence of infectious virus supports the need for isolation and assessment of longer treatment...

Plasma metabolome and cytokine profile reveal glycylproline modulating antibody fading in convalescent COVID-19 patients
Source : https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9407385/
Zhu Yang, a , b , c , 1 Di Wu, d , e , 1 Shanxin Lu, a , b , 1 Yang Qiu, d , e , 1...
Significance: Using absolute quantification of both cytokines and metabolites from the plasmas of convalescent COVID-19 patients, machine-learning approaches identified that a combination of cytokines and metabolites can clearly discriminate convalescent patients with rapidly faded antibodies (CO) from ordinary convalescents with antibodies...
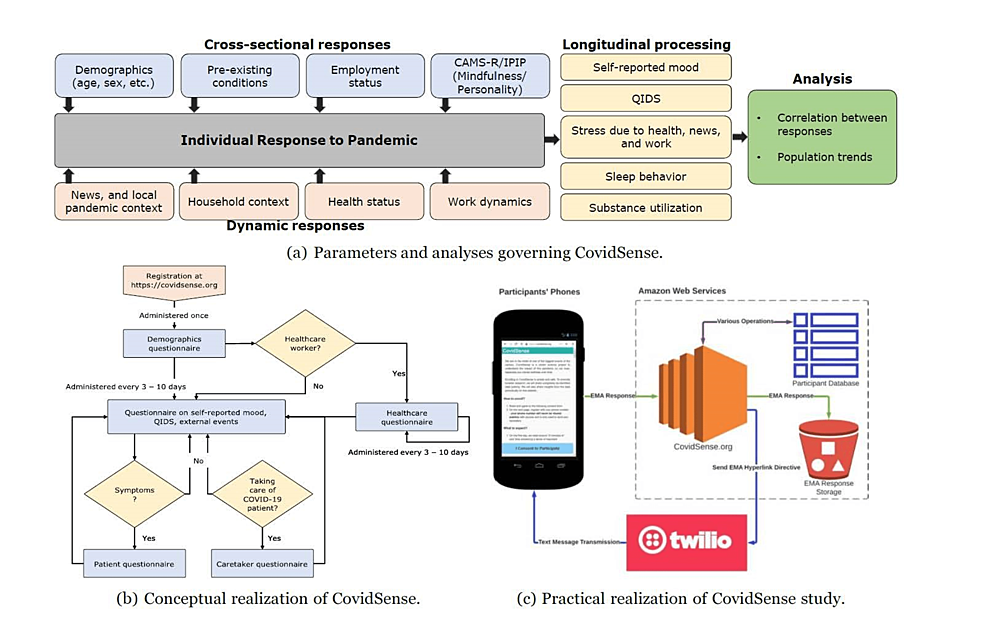
Evolution of Mood Symptomatology Through the COVID-19 Pandemic: Findings From the CovidSense Longitudinal Study
Background The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 global pandemic, with its associated coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) illness, has led to significant mental, physical, social, and economic hardships. Physical distancing,...
Conclusions:The effects of pandemic-related chronic stress were predominant in young adults and individuals with pre-existing mental and medical conditions regardless of whether they had acquired COVID-19 or not. These results point to the possibility of allocating preventive as well as treatment resources based on vulnerability.

SARS-CoV-2 disrupts respiratory vascular barriers by suppressing Claudin-5 expression
Source : https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9491726/
Rina Hashimoto, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing - original draft, 1 , † Junya Takahashi, Formal analysis, Investigation, Validation, Visualization, Writing - original draft, Writing - review & editing,...
We concluded that the down-regulation of CLDN5 expression is a pivotal mechanism for SARS-CoV-2–induced endothelial barrier disruption in respiratory organs and that inducing CLDN5 expression is a therapeutic strategy against COVID-19.

