
High-Dose vs Standard-Dose Vitamin D Supplementation in Older Adults With COVID-19 (COVIT-TRIAL)
Source : https://www.practiceupdate.com/expertopinion/6028/2/6
Written by Irene Mace Hamrick MD, FAAFP, AGSF
While other studies have shown benefit from vitamin D in COVID,10 the NIH states insufficient evidence either for or against the use of Vitamin D in COVID.11 I think it is reasonable to give a high dose once in this setting; however, I do not advocate intermittent high-dose vitamin D because of increased risk of fracture and falls.12,13 I do...
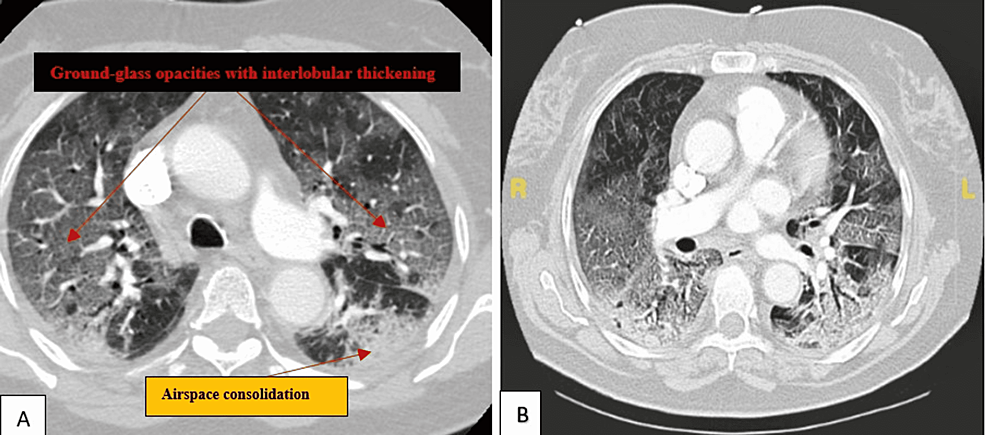
Radiological Finding of Crazy-Paving Pattern in COVID-19 Pneumonia
The recent global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has brought many radiographic findings in other respiratory disease processes. One of these radiological findings is crazy paving. This paper discusses...
Chest CT showed ground-glass opacities and interlobular septal thickening consistent with a crazy-paving appearance. As part of the common CT findings of patients with active COVID-19 infection, crazy paving should prompt the interpreting radiologist to consider COVID-19 pneumonia as part of the differential.

Blood and saliva SARS-CoV-2 antibody levels in self-collected dried spot samples - Medical Microbiology and Immunology
Source : https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00430-022-00740-x
We examined the usefulness of dried spot blood and saliva samples in SARS-CoV-2 antibody analyses. We analyzed 1231 self-collected dried spot blood and saliva samples from healthcare workers. Participants filled...
Self-collected dry blood and saliva spot samples combined with the GSP/DELFIA technique comprise a valuable tool to investigate an individual’s immune response to SARS-CoV-2 exposure or vaccination. Saliva IgG has high potential to monitor vaccination response wane, since the sample is non-invasive and easy to collect.
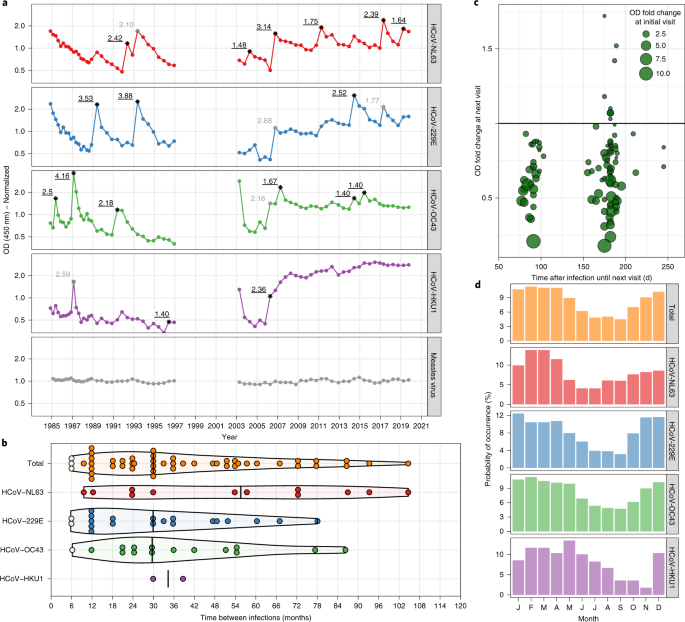
Seasonal coronavirus protective immunity is short-lasting - Nature Medicine
Source : https://www.nature.com/articles/s41591-020-1083-1
The durability of immunity to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is unknown. Lessons from seasonal coronavirus infections in humans show that reinfections can occur within 12 months of...
Insights from infections with the four seasonal human coronaviruses might reveal common characteristics applicable to all human coronaviruses. We monitored healthy individuals for more than 35 years and determined that reinfection with the same seasonal coronavirus occurred frequently at 12 months after infection.
Interpretation: ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 is well tolerated and immunogenic in children aged 6–17 years, inducing concentrations of antibody that are similar to those associated with high efficacy in phase 3 studies in adults. No safety concerns were raised in this trial.

