
Cognitive Disengagement Syndrome and Child Sleep Problems in ADHD, Anxiety and Depression - PubMed
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37510463/
The main objective of this study was to analyse the relationship and differential contribution of Cognitive Disengagement Syndrome (CDS) and sleep problems in children in different psychopathological measures. A total...
Conclusion: The data indicate the importance of sleep problems in understanding CDS and its relationship with other psychopathological measures, especially ADHD, although to a greater extent with internalising symptoms, especially DEP.

Serdexmethylphenidate/dexmethylphenidate effects on sleep in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder - PubMed
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37426086/
In this analysis of children taking SDX/d-MPH for ADHD, sleep problems did not worsen based on the mean CSHQ total sleep disturbance score. Statistically significant improvements in most CSHQ sleep...
Conclusion: In this analysis of children taking SDX/d-MPH for ADHD, sleep problems did not worsen based on the mean CSHQ total sleep disturbance score. Statistically significant improvements in most CSHQ sleep domains were observed after 1 month and lasted for up to 12 months of treatment.
-
 ADHD Connect2yrKey Points • Source: Frontiers in Psychiatry • Conclusion: “In this analysis of children taking SDX/d-MPH [serdexmethylphenidate/dexmethylphenidate] for ADHD, sleep problems did not worsen based on the mean CSHQ total sleep disturbance score. Statistically Show More
ADHD Connect2yrKey Points • Source: Frontiers in Psychiatry • Conclusion: “In this analysis of children taking SDX/d-MPH [serdexmethylphenidate/dexmethylphenidate] for ADHD, sleep problems did not worsen based on the mean CSHQ total sleep disturbance score. Statistically Show More
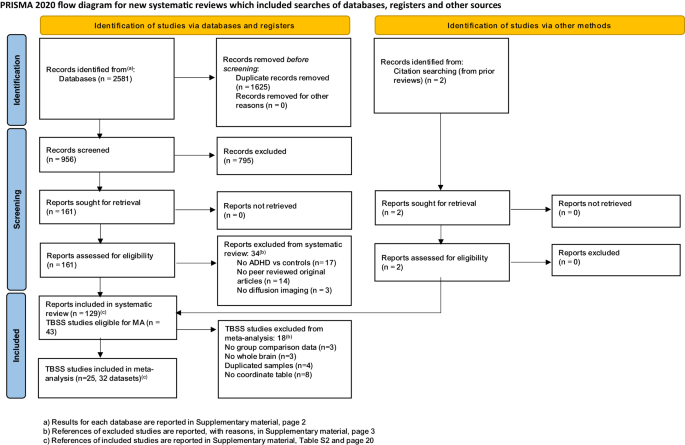
White matter alterations in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): a systematic review of 129 diffusion imaging studies with meta-analysis - Molecular Psychiatry
Source : https://www.nature.com/articles/s41380-023-02173-1
Aberrant anatomical brain connections in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) are reported inconsistently across diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) studies. Based on a pre-registered protocol (Prospero: CRD42021259192), we searched PubMed, Ovid, and Web...
Conclusions/Relevance: Absence of findings in children may be related to the late development of callosal fibers, which may enhance case-control differences in adulthood. Clinicodemographic and methodological differences were major barriers to consistency and comparability among studies, and should be addressed in future investigations.

Distinct effects of different neurofeedback protocols on the neural mechanisms of response inhibition in ADHD
Source : https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1388245723006545?via=ihub
In attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), impaired response inhibition is frequently observed. A promising non-pharmacological treatment is ...
Significance: These effects shed further light on the oscillatory dynamics underlying cognitive control in ADHD and how these may be targeted in neurofeedback treatments.

The short and long-term effects of a lifestyle intervention in children with mental illnesses: a randomized controlled trial (Movementss study) - BMC Psychiatry
Source : https://bmcpsychiatry.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12888-023-04884-9
Background A lifestyle including poor diet, physical inactivity, excessive gaming and inadequate sleep hygiene is frequently seen among Dutch children. These lifestyle behaviors can cause long-term health problems later in...
Conclusions/Relevance: This paper describes the rationale, study design, and methods of an ongoing randomized controlled trial (RCT) comparing the short-term (12 weeks) and long-term (1 year) effects of a lifestyle intervention with care as usual (CAU) in children with MI and an unhealthy lifestyle.
