
Monoclonal Antibodies for Treatment of SARS-CoV-2 Infection During Pregnancy
Source : https://doi.org/10.7326/M22-1329
If the address matches an existing account you will receive an email with instructions to reset your password.
Conclusion: In pregnant persons with mild to moderate COVID-19, adverse events after mAb treatment were mild and rare. There was no difference in obstetric-associated safety outcomes between mAb treatment and no treatment among persons who delivered. There was no difference in 28-day COVID-19–associated outcomes and non-COVID-19–related...
Effectiveness of mRNA-1273, BNT162b2, and BBIBP-CorV vaccines against infection and mortality in children in Argentina, during predominance of delta and omicron covid-19 variants: test negative, case-control study
Source : https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj-2022-073070
Objective To estimate the effectiveness of a two dose vaccine schedule (mRNA-1273, BNT162b2, and BBIBP-CorV) against SARS-CoV-2 infection and covid-19 related death and short term waning of immunity in children...
Conclusion: Our study highlights that a probability score for GCA derived from a large multi-centre cohort of patients who were biopsy positive predicts ultrasound positivity with similar accuracy. Our work reveals that scoring systems are not infallible but can be helpful in guiding clinical decision making.

Incidence of Viral Rebound After Treatment With Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir and Molnupiravir - PubMed
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36472873/
In this cohort study, viral rebound was uncommon in patients taking molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir-ritonavir and was not associated with increased risk of mortality. Given these findings, novel oral antivirals should...
Conclusions and Relevance: In this cohort study, viral rebound was uncommon in patients taking molnupiravir or nirmatrelvir-ritonavir and was not associated with increased risk of mortality. Given these findings, novel oral antivirals should be considered as a treatment for more patients with COVID-19 in the early phase of the infection.
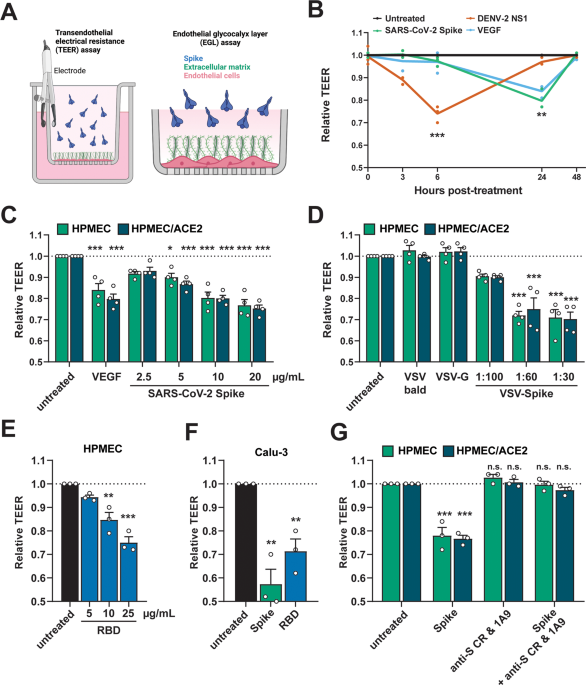
SARS-CoV-2 Spike triggers barrier dysfunction and vascular leak via integrins and TGF-β signaling - Nature Communications
Source : https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-34910-5
Severe COVID-19 is associated with epithelial and endothelial barrier dysfunction, however, the molecular pathways resulting in endothelial barrier dysfunction and vascular leakage are only sparsely understood. Here, Biering et al....
Our findings offer mechanistic insight into SARS-CoV-2-triggered vascular leak, providing a starting point for development of therapies targeting COVID-19.
Highlights:
- Potent main protease inhibitors, which block SARS-CoV-2 infection, were developed
- Our strategy adopted fluorine scan and amide surrogate replacement in molecules
- The antiviral activity of the top compound is higher than that of Nirmatrelvir
- Some compounds have remarkably preferable pharmacokinetics in mice

