SARS-CoV-2 ORF7a potently inhibits the antiviral effect of the host factor SERINC5 - Nature Communications
Source : https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-022-30609-9
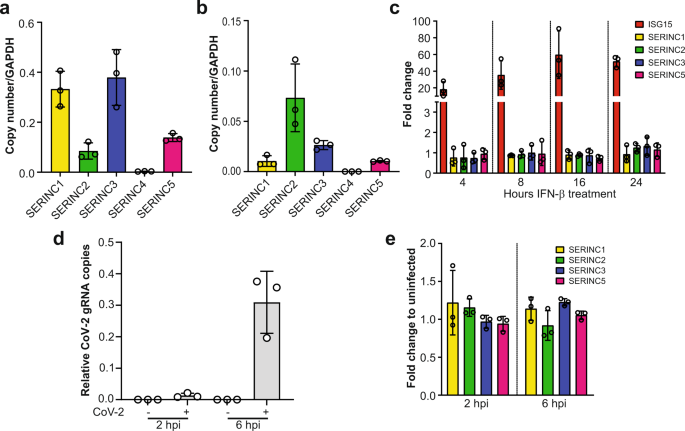
SERINC5, is a cellular multipass transmembrane protein involved in sphingolipid and phosphatydilserine biogenesis and a known retroviral restriction factor. Here, Timilsina et al. show that SERINC5 is a host restriction...
Here, we show SERINC5 inhibits SARS-CoV-2 entry by blocking virus-cell fusion, and SARS-CoV-2 ORF7a counteracts the antiviral effect of SERINC5 by blocking the incorporation of over expressed SERINC5 in budding virions.

Single-cell transcriptomics reveal a unique memory-like NK cell subset that accumulates with ageing and correlates with disease severity in COVID-19 - Genome Medicine
Background Natural killer (NK) cells are innate lymphoid cells that mediate antitumour and antiviral responses. However, very little is known about how ageing influences human NK cells, especially at the...
Conclusions: We identified a unique memory-like NK cell subset that accumulates with ageing and correlates with disease severity in COVID-19. Our results identify memory-like NK2.1 cells as a potential target for developing immunotherapies for infectious diseases and for addressing age-related dysfunctions of the immune system.
Clofoctol inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication and reduces lung pathology in mice
Source : https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1010498
Author summary Antivirals targeting SARS-CoV-2 are sorely needed. In this study, we screened a library of approximately 2000 drug compounds that have been used or are still used in the...
Notably, the peak concentration of clofoctol that can be achieved in human lungs is more than 20 times higher than its IC50 measured against SARS-CoV-2 in human pulmonary cells. This compound inhibits SARS-CoV-2 at a post-entry step. Lastly, therapeutic treatment of human ACE2 receptor transgenic mice decreased viral load, reduced inflammatory...
Pathophysiological pathway differences in children who present with COVID-19 ARDS compared to COVID -19 induced MIS-C - Nature Communications
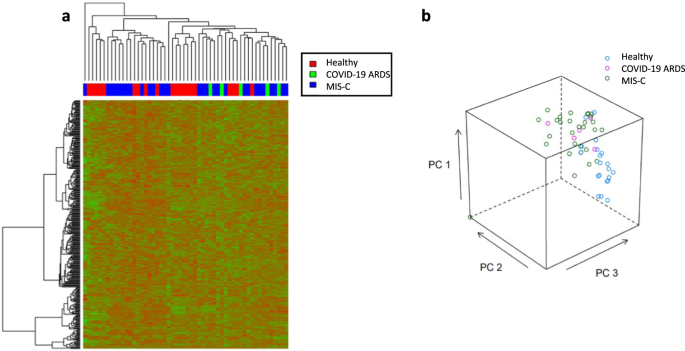
COVID-19 has infected more than 275 million worldwide (at the beginning of 2022). Children appear less susceptible to COVID-19 and present with milder symptoms. Cases of children with COVID-19 developing...
Complement and coagulation activation are implicated in these clinical phenotypes, however there was significant contribution of FcGR and BCR activation in MIS-C and scavenging of haem and retinoid metabolism in COVID-19 ARDS. We show global proteomic differences in MIS-C and COVID-ARDS, although both show complement and coagulation...
The Mysterious Risk of Arterial Thrombosis With COVID-19: A Case Series and Systematic Review of Acute Limb Ischaemia
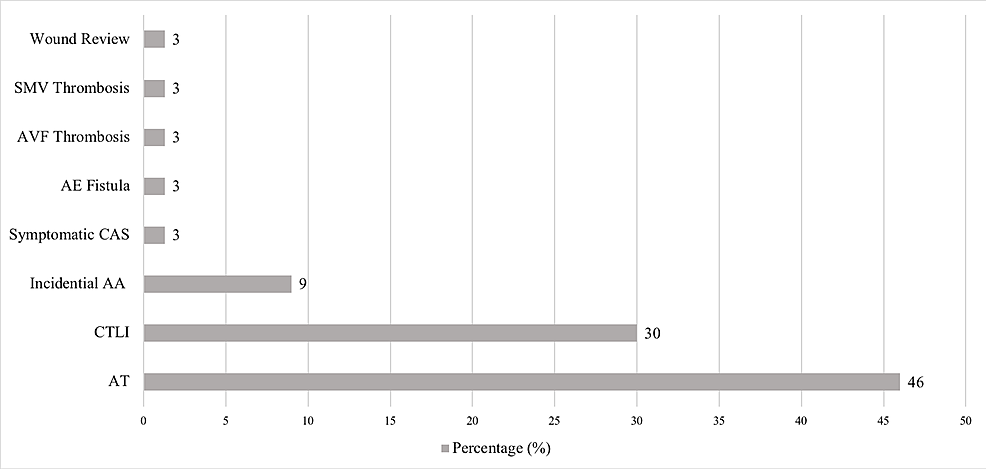
Introduction: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) generates a cytokine storm that predisposes patients to systemic complications including arterial thrombosis (AT) and acute limb ischaemia (ALI). This study reviews our understanding of...
Conclusions: The incidence of AT within the vascular surgery territory in COVID-19 patients is low; however, it is associated with poor 30-day AFS. A computed tomography angiography protocol including the entire major vessels may be indicated in COVID-19 patients.

