Newly-discovered antibodies can neutralize COVID-19 variants, potentially prevent future coronavirus outbreaks
Source : https://www.eurekalert.org/news-releases/997045
Scientists have isolated potent neutralising antibodies from a COVID-19 vaccinated SARS survivor that exhibited remarkable breadth against known sarbecoviruses. The antibodies targeted a conserved region of the spike protein and...
The most powerful antibody, named E7, neutralised both SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2 sarbecoviruses, animal sarbecoviruses and newly emerged SARS-CoV-2 variants, such as Omicron XBB.1.16. It was shown to neutralise via a unique mechanism of binding that bridges two parts of the coronavirus’ spike protein that it uses to invade cells. This appears...

Adverse Events of Latent Tuberculosis Treatment With Isoniazid in People Living With HIV: A Case-Control Study in a Resource-Rich Setting
Introduction Multiple risk factors, such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection and immunosuppressive therapies, increase the odds of latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI) reactivation and progression to active tuberculosis. A six-to-nine-month...
In our study, INH-associated AEs were common, with liver toxicity being the most frequent. Older age, economic hardship, and excessive alcohol consumption increased the odds of INH-associated AEs, while PLHIV had lower odds of developing INH-associated AEs, even when adjusting for other variables in the multivariate analysis. Further studies...
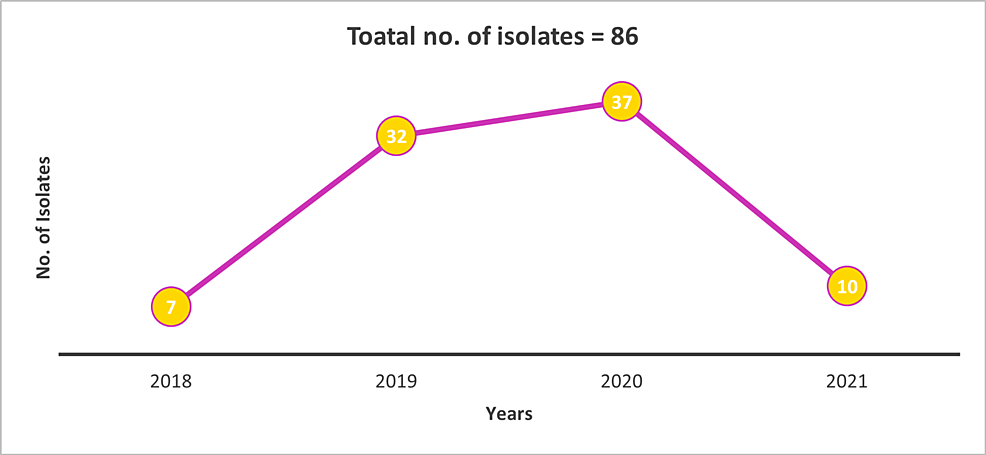
A Multicenter Evaluation of Overall Susceptibility and Antimicrobial Resistance Among Streptococcus pneumoniae Isolates
Purpose: S. pneumoniae ranks as the fourth-most lethal pathogen globally in terms of fatalities associated with or attributable to resistance. In this study, the Antimicrobial Testing Leadership and Surveillance (ATLAS)...
Conclusion: An increase in resistance to penicillin and macrolides among S. pneumoniae isolates was observed in the Indian population. Addressing the elevating rates of S. pneumoniae resistance may require pneumococcal conjugate vaccines (PCVs) with expanded serotype coverage and targeted antimicrobial stewardship efforts.
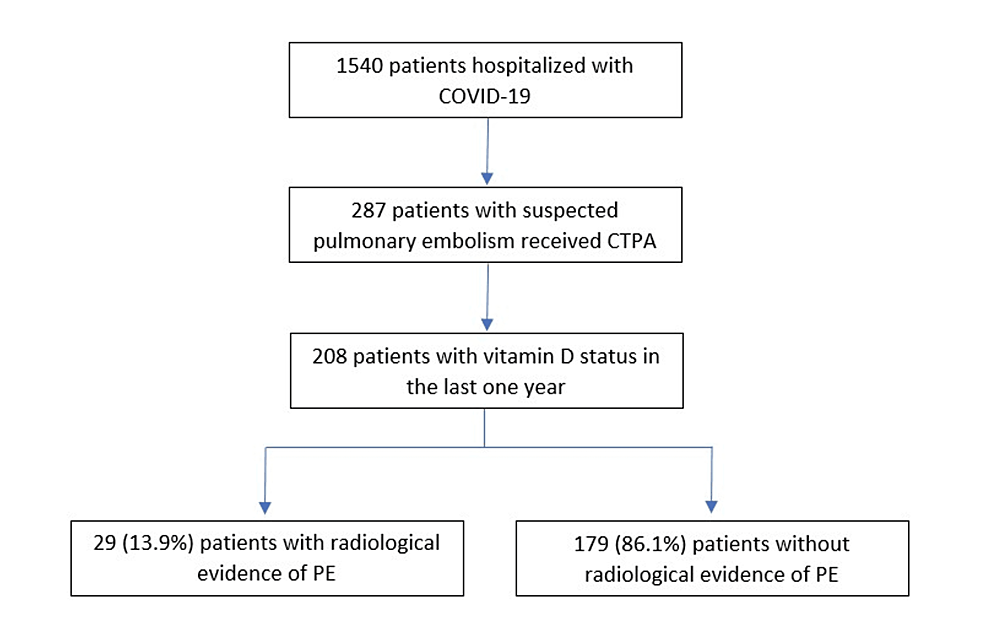
A Retrospective Analysis of Vitamin D Levels in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients With Suspected Pulmonary Embolism
Introduction Despite using anti-coagulation therapy in hospitalized coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients, they have high rates of pulmonary embolism (PE) and deep vein thrombosis (DVT). The main objective of this...
Conclusions: This study found no association between vitamin D deficiency and the occurrence of a new PE or DVT in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Patients with vitamin D deficiency were more likely to be admitted to the ICU and had increased overall mortality.
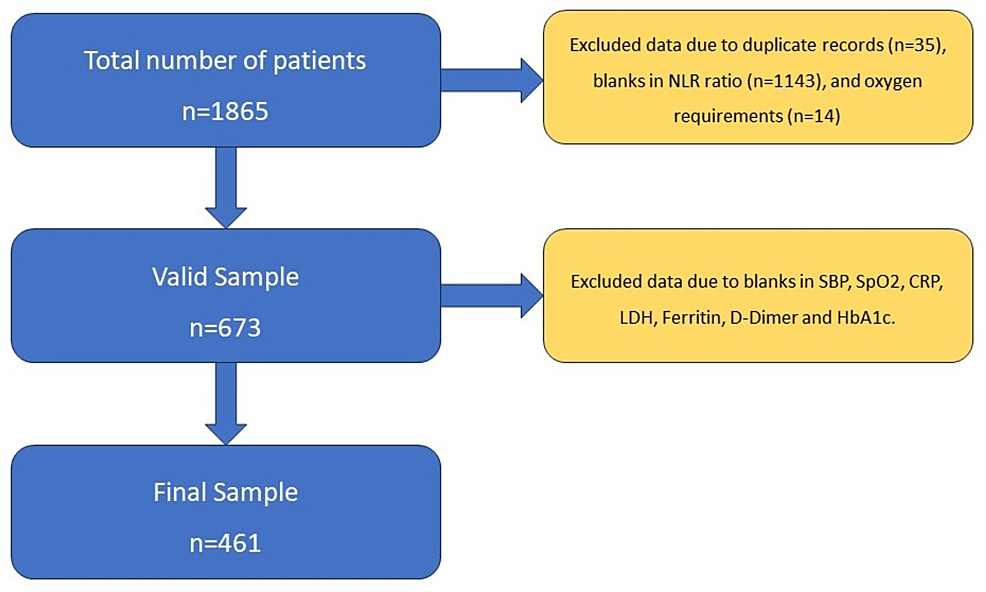
Changes and Rate of Change in Neutrophil-Lymphocyte Ratio (∆NLR) as an Early Prognostic Marker for the Severity of Outcomes in Patients With COVID-19 and Its Applicability in Other Viral and Bacterial Diseases
Introduction: COVID-19 is a global pandemic that has spread rapidly and resulted in numerous deaths worldwide. Many inflammatory markers such as neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), D-dimer, serum ferritin, C-reactive protein (CRP),...
Conclusion: An independent predictor of the poor prognosis of COVID-19 is the severity of the disease in the initial one or two days. ∆NLR is a unique marker, and its scope of use in other disorders’ prognoses must be further researched. The prediction models also help us in decision-making strategies and also prepare us for future...

