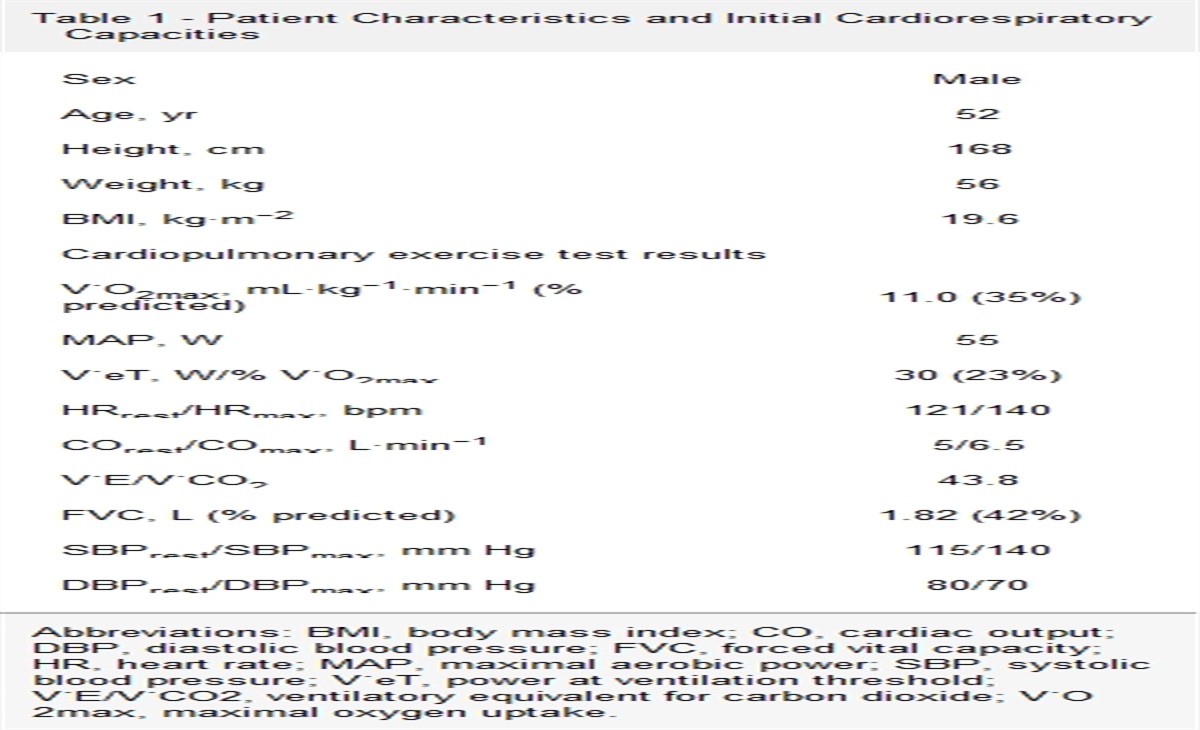
Prehabilitation Using a Cardiac Rehabilitation Program for a Patient With a Total Artificial Heart Prior to Heart Transplantation
This technology aims to address the various subsequent shortfalls of organs. This report reviews the impact of a prehabilitation on a patient with an Aeson TAH (Carmat). Discussion: We assessed...
Similar functional improvements were observed over a short period of 2 weeks compared with a longer protocol for patients with heart transplant.

Prognostic Implication of Heart Failure Stage and Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction for Patients With In-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: a 16-Year Retrospective Cohort Study
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38407585/
HF stage and LVEF could stratify patients with IHCA into different prognoses. Pre-HF and HFpEF were significantly associated with favorable neurological and survival outcomes after IHCA. Further studies are warranted...
Pre-HF and HFpEF were associated with better neurologic and survival outcomes compared with general in-hospital cardiac arrest.

Cost-Effectiveness of a Multidimensional Post-Discharge Disease Management Program for Heart Failure Patients-Economic Evaluation Along a One-Year Observation Period
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38353683
The economic evaluation along the cohort study showed that the HerzMobil Tirol is very cost-effective compared to UC and cost-saving in a sensitivity analysis correcting for "non-HF related costs." These...
A 3-month telemedicine-assisted transitional care service for patients with advanced HF was highly cost effective and improved health outcomes when compared with usual care.

Sex-Related Differences in Patients Presenting With Heart Failure-Related Cardiogenic Shock
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38353681/
In this large HF-CS registry, sex disparities in risk factors and clinical presentation were observed. Despite these differences, the use of treatments was comparable, and both sexes exhibited similarly high...
Women tended to be older but had fewer cardiovascular risk factors and were less likely to present with prevalent HF, a severely depressed LVEF, or with renal dysfunction.
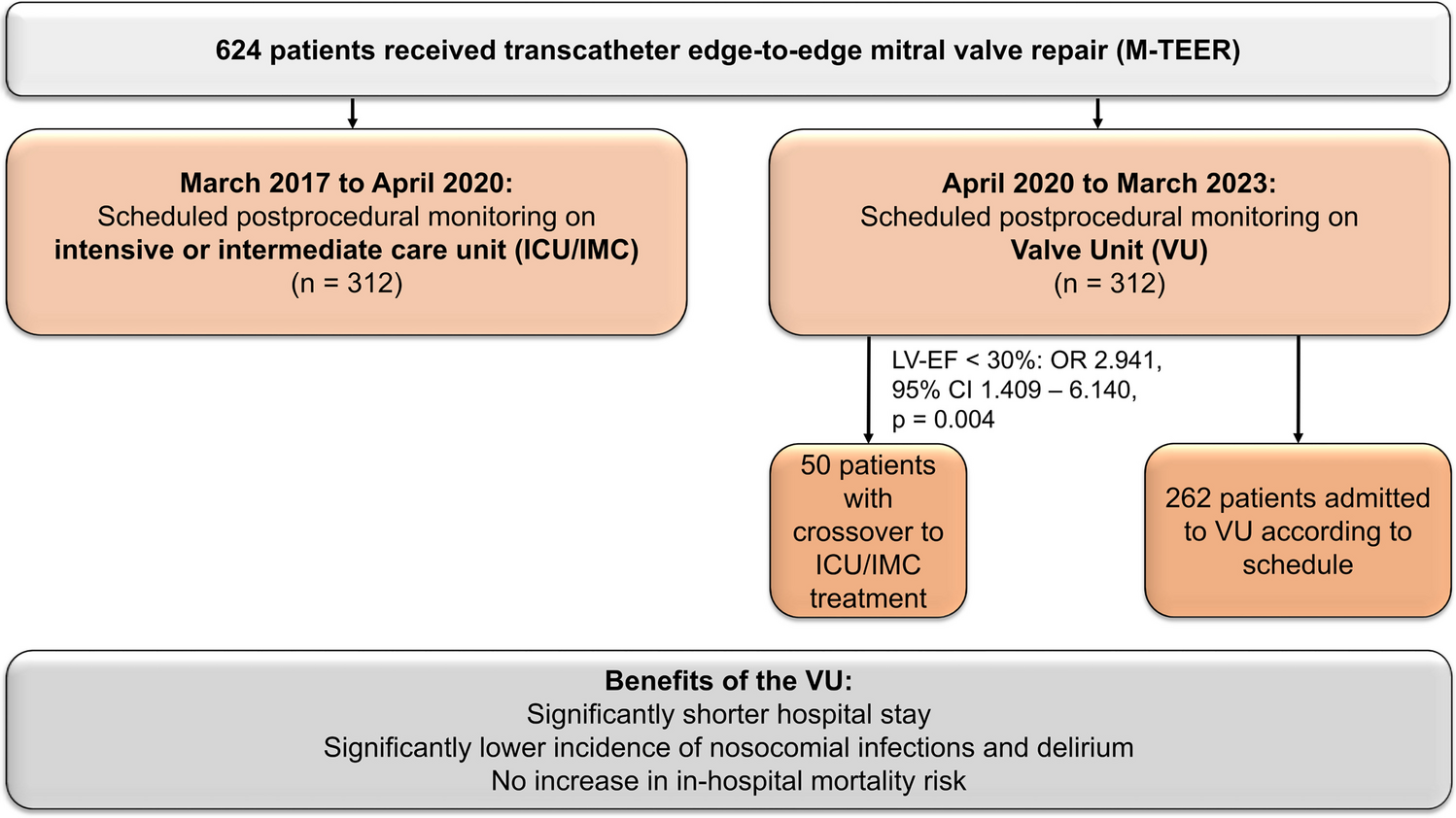
Valve Unit Instead of Intensive or Intermediate Care Unit Admission Following Transcatheter Edge-to-Edge Mitral Valve Repair Is Safe and Reduces Postprocedural Complications
Source : https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00392-024-02384-8
Transcatheter edge-to-edge mitral valve repair (M-TEER) is often performed in general anesthesia, and postprocedural monitoring is usually warranted on an intensive or intermediate care unit (ICU/IMC). We evaluated the implications...
Immediate admission to the valve unit instead of primary ICU/IMC treatment after M-TEER was associated with a significantly shorter hospital stay and a lower incidence of infections and delirium.

