
Association Between Dietary Insulin Index and Load With Cardiometabolic Risk Factors and Risk of Metabolic Syndrome Among the Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: a Cross-Sectional Study
Source : https://bmcnutr.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40795-023-00803-z
This study aims to investigate the association between dietary insulin index (DII) and load (DIL) with cardiometabolic risk factors and the risk of developing metabolic syndrome (MetS) among patients with...
Participants in the highest quartiles of both dietary insulin index and load demonstrated higher odds of metabolic syndrome, hyperglycemia, and increased waist circumference.

Walking Speed and the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Source : https://bjsm.bmj.com/content/early/2023/11/14/bjsports-2023-107336
We included cohort studies that explored the association between walking speed and the risk of type 2 diabetes in adults.
Dose–response analysis suggested that the risk of type 2 diabetes decreased significantly at a walking speed of 4 km/hour and above.

Association Between Serum Osteocalcin and Atherosclerosis in Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus: a Cross-Sectional Study
Source : https://bmcendocrdisord.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12902-023-01462-8
The past few decades have seen a marked increase in the macrovascular complications of Type-2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) such as coronary heart disease, peripheral arterial disease, and cerebrovascular disease. This...
The study found that serum osteocalcin was lower in individuals with higher carotid intima-media thickness showing a significant negative association between atherosclerosis and serum osteocalcin levels in patients with T2DM.
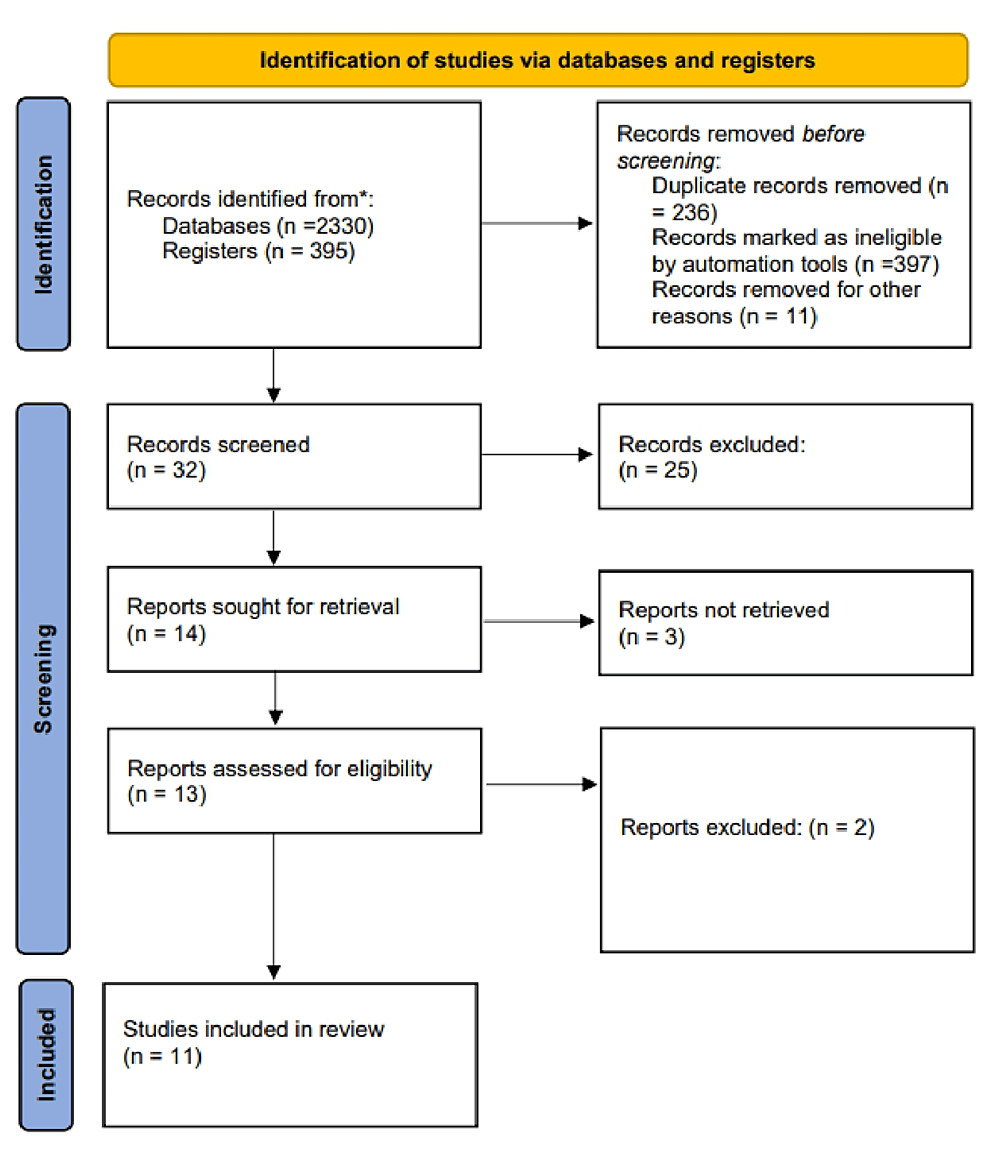
The Link Between Sleeping and Type 2 Diabetes: a Systematic Review
Adults should get at least seven hours of sleep each night to preserve their overall health and well-being. Sleep disorders and other sleep-related issues affect a sizeable portion of the...
People with type 2 diabetes frequently experience sleep disturbances. To eventually improve health and quality of life, efforts should be taken to diagnose and treat sleep disturbances in patients with type 2 diabetes, as doing so may prevent diabetes from progressing.

Comparison of 10 × 1-Minute High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) Versus 4 × 4-Minute HIIT on Glucose Control and Variability in Females With Type 2 Diabetes
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38052023/
Two high-intensity interval training (HIIT) regimens are often used in research and clinical settings. Yet there has been no direct comparison to determine if one can improve glucose control and...
Exploratory analyses focusing on individuals with poor glucose control revealed that 24-hour mean glucose, glucose variability, and peak glucose were lower following HIIT10 versus controls, whereas HIIT4 reduced time spent in moderate hyperglycemia versus controls.

