
Guanfacine for the Treatment of Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis - PubMed
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36944092/
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure....
Conclusions: Guanfacine is safe and effective for treating ADHD, with no serious adverse events. Guanfacine should be considered as an effective treatment option where effectiveness or tolerability of the central nervous system stimulant is of concern. There is stronger evidence of efficacy for children; more clinical studies are needed...

Treatment with methylphenidate and the risk of fractures among children and young people: a systematic review and self-controlled case series study - PubMed
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36918367/
In conclusion, methylphenidate treatment may lower the risk of all-cause fractures from both study designs, however, further evidence is needed about the treatment duration and sex effect. Conclusions on stress...
Conclusion: In conclusion, methylphenidate treatment may lower the risk of all-cause fractures from both study designs, however, further evidence is needed about the treatment duration and sex effect. Conclusions on stress fractures are not yet established and further research is required.

Discontinuation of methylphenidate after long-term exposure in nonhuman primates
Source : https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0892036223000235?via=ihub
The neurotoxic effects of withdrawal of methylphenidate following long-term use on the developing central nervous system was investigated. * Discontinuation after chronic exposure was not associated with significant changes in...
Conclusions/Relevance: Discontinuation after chronic exposure was not associated with significant changes in brain metabolism and monoamine function.
-
 ADHD Connect2yrKey Points • Source: Neurotoxicology and Tetralogy • Conclusions/Relevance: “This study demonstrates that 6 months after cessation of long-term, chronic MPH [methylphenidate] treatment, there are no significant neurochemical or neural metabolic changes Show More
ADHD Connect2yrKey Points • Source: Neurotoxicology and Tetralogy • Conclusions/Relevance: “This study demonstrates that 6 months after cessation of long-term, chronic MPH [methylphenidate] treatment, there are no significant neurochemical or neural metabolic changes Show More
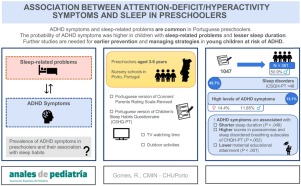
Association between attention-deficit/hyperactivity symptoms and sleep in preschoolers
Source : https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S234128792300025X?via=ihub
Available online 15 March 2023 Author links open overlay panel Rita Gomes a , , , , , Show more Sleep problems are frequent in children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)....
Conclusions: ADHD and sleep disorders are common in preschoolers, in Porto, and this study suggests some clinical correlations between them. Since these interactions are complex and far from being elucidated, further studies are paramount to provide guidance for prevention and managing strategies in younger children at risk for ADHD.

Prescribing patterns for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder among children and adolescents in Taiwan from 2004 to 2017
Source : https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0929664623000670?via=ihub
This study documented the prescribing patterns of methylphenidate and atomoxetine among patients aged 3 to 18 in Taiwan diagnosed with attention defic...
Conclusion: Methylphenidate was the predominant treatment for ADHD in 2004–2017. However, the prevalence of pharmacotherapy for ADHD was relatively low. Further investigation on the reasons behind this pattern is recommended.
